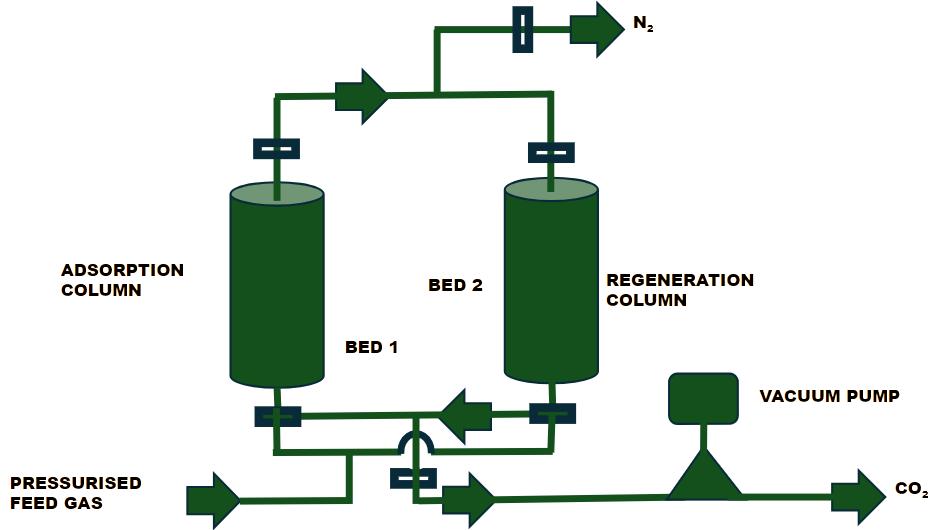
1. Amine scrubbing process
This is a post-combustion carbon capture technology in which an amine solvent is used to absorb CO₂ from flue gas. The absorbed CO₂ in the absorber column is then released (desorbed) in the stripper using high energy (temperature). The regenerated CO₂-free amine solvent (lean amine) is recycled back to the absorber. The captured CO₂ is then compressed and reused for other applications. Although this is a mature and highly efficient technology, it is expensive due to the high energy required for solvent regeneration.1
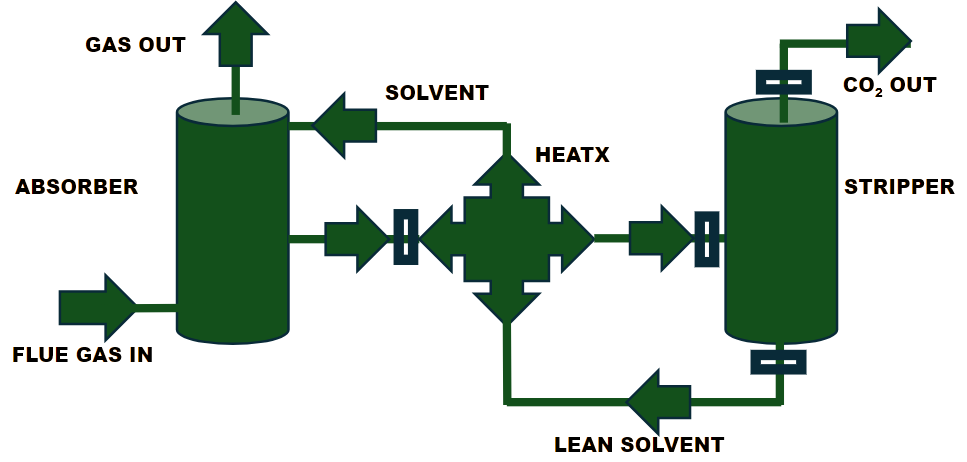
2. Calcium looping process
It is a promising technology for capturing CO₂ from high-temperature industrial sources as well as for direct air capture from the atmosphere. In this process, calcium oxide (CaO) in the absorber column reacts with CO₂ to form calcium carbonate (CaCO₃, or limestone). This reaction is reversible: in the stripper (or calciner) column, the limestone is heated to high temperatures to release CO₂ and regenerate CaO. The regenerated CaO is then reused to capture CO₂ again, completing the cyclic process.2
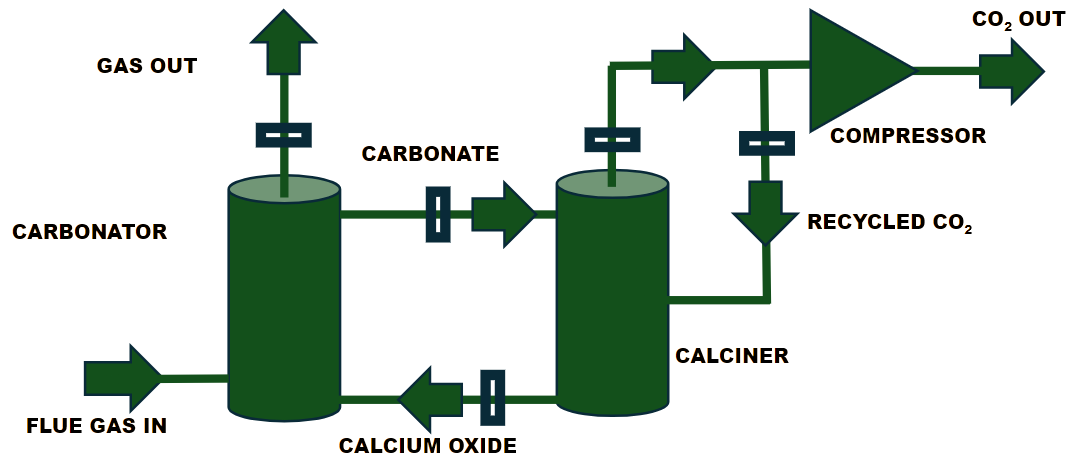
3. Swing adsorption process
This technology is based on solid adsorbents that can selectively capture CO₂. As the feed air flows through a packed bed, CO₂ is adsorbed onto the sorbent surface. A combination of mild heating and reduced pressure is then applied to desorb the CO₂, making this a scalable and sustainable method for removing CO₂ from the atmosphere.3